Unlock Understanding: What Is the Autism Spectrum Disorder

Navigating the world of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can feel overwhelming, right?
There's so much information out there, and it's hard to know where to start. Maybe you're wondering what is autism caused by, or perhaps you're trying to explain what is autism for kids in a way they can understand. You might even be searching for helpful tools like cognitive games to support development.
This article is here to help you unpack it all. We're going to dig into all the different aspects of ASD, covering everything from what people call "high-functioning" to the levels 1 through 3, and even talk about PDA and nonverbal autism. We'll look at the usual symptoms you see, the whole deal with masking and scripting, and even get into that tricky debate around ABA therapy.

What Is the Definition of Autism
The thing to remember is that it's not one single thing, but a spectrum. We're talking about a group of developmental conditions that affect how a person interacts with the world, communicates, and behaves. It's all about differences in brain development.
General Characteristics of ASD |
|
Defining and Its Classification |
|
Spectrum |
|
And also it's important to note that while research continues, what is the cause of autism is still complex and most likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Causes
So, you're probably wondering what is causing autism, right? It's one of the most common questions, and honestly, the answer is complex. We don't have a single, definitive explanation, but research points to a combination of factors. It's important to understand that what exactly is autism involves different factors playing together.
Genetic Factors
Role of Genes | Genetics play a significant role, but it's not as simple as "one gene." Instead, it's likely that many different genes contribute, each with a small effect. | Explanation: Think of it like height. Many different genes influence how tall you are, and each gene contributes a little bit. It's the same with autism. |
Variations | Some individuals with it have specific genetic variations that are known to be associated with the condition. These variations can affect brain development and function. | Examples: Chromosomal abnormalities (like Fragile X syndrome), single-gene mutations. |
Family | It tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. If one child in a family has autism, the risk of having another child with it is higher. | A family history of autism doesn't guarantee that a child will develop autism. It simply increases the risk. |
Myths
It's essential to address common misconceptions about the causes of autism.
Myth: It is caused by vaccines.
Myth: It is caused by "refrigerator mothers" (cold and uncaring parenting).
Myth: It is caused by bad food.
The Importance of Reliable Information: It's crucial to rely on credible sources of information about autism, such as:
Scientific research articles.
Reputable autism organizations.
Medical professionals.

What kind of disability is autism?
Understanding that autism is a neurodevelopmental condition, not a result of personal shortcomings or external factors like bad parenting, is critical for fostering acceptance and effective support.
It highlights the need for understanding and support, and combats stigma.
What Is Autism Classified As
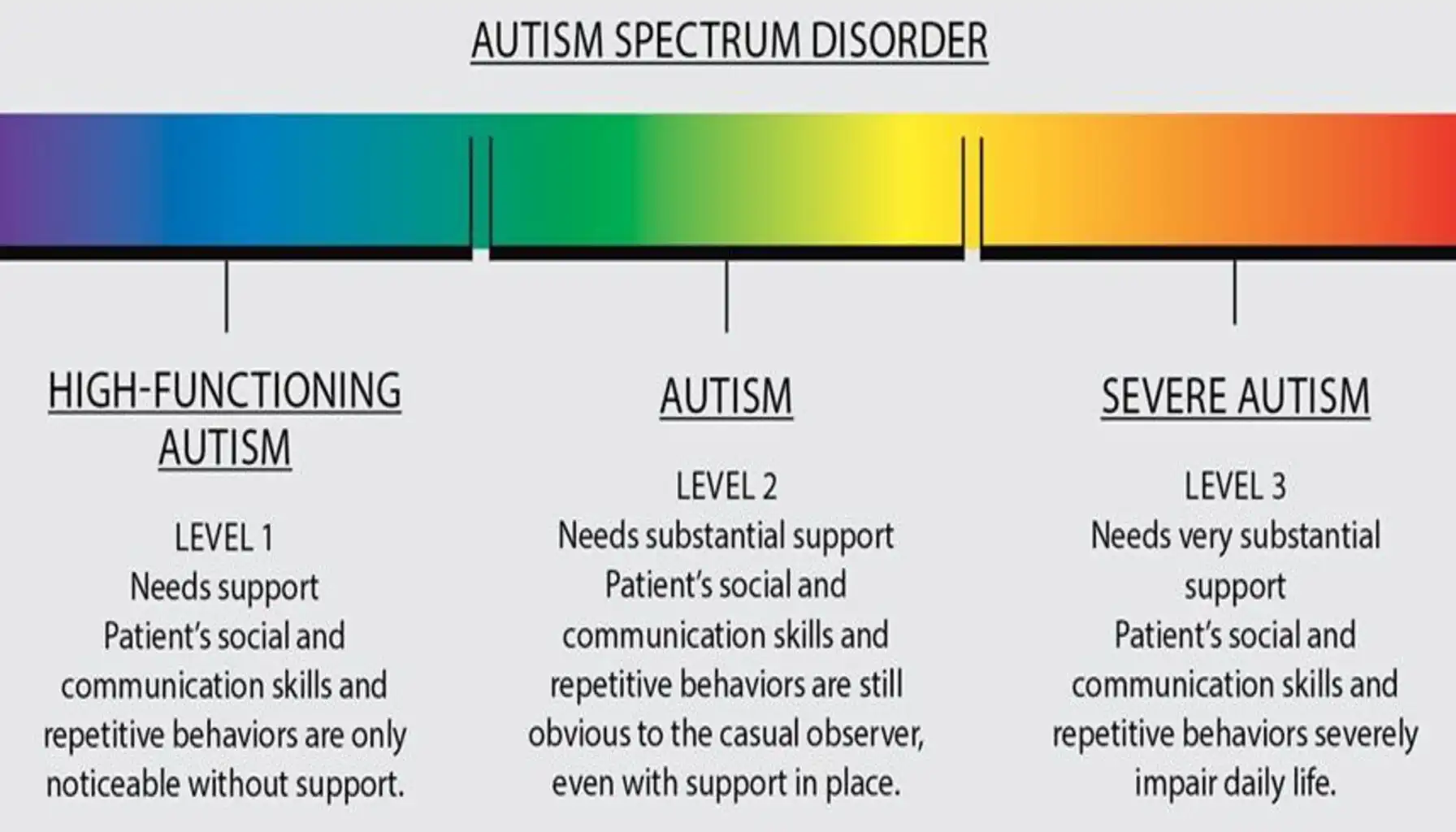
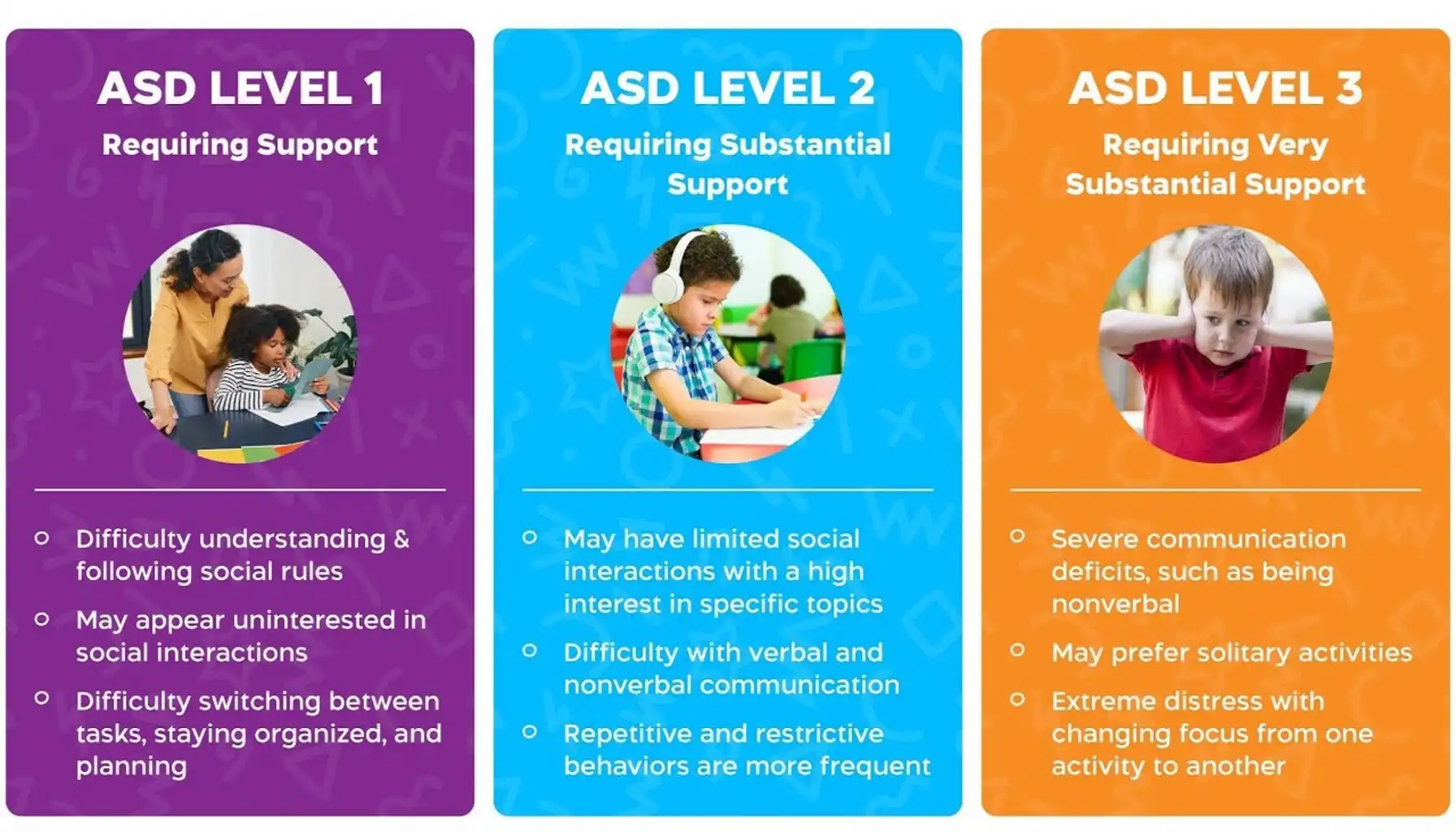
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) uses levels to describe the intensity of support someone with ASD needs. These levels are based on difficulties with social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. It's important to remember that levels aren't fixed labels, and a person's support needs can change over time.
What is Level 1 Autism? |
|
What is Level 2 Autism? | At what is level 2 autism, individuals have more significant difficulties with social communication and interaction. Their restricted, repetitive behaviors are also more pronounced and interfere more with daily life. They may have difficulty understanding nonverbal cues, limited speech, and struggle with change. They often require more support than individuals at Level 1, especially in social settings and when managing morning routines. |
What is Level 3 Autism? |
|
Specific Types
What is High Functioning Autism?
The term "high-functioning autism" isn't officially in the DSM-5, but it's used for people with ASD who are bright and good with words.
They often live independently and work, but still struggle with social skills, sensory issues, or planning.
That's why understanding what is masking autism, and how they hide these struggles, is so important - it helps us see the full picture.
What is Nonverbal Autism?
When we say someone has "nonverbal autism," it means they have limited or no spoken language. But it's so important to remember that "nonverbal" doesn't mean they can't communicate.
They might use gestures, sign language, pictures, or even special technology to get their message across.
Awareness and Understanding
Ever wonder what color is autism awareness? It's blue. Blue has become a symbol of support and acceptance for people with autism, and you'll often see it used during what month is autism awareness month, which is April. April is a time for communities to come together, share stories, and promote understanding and inclusion.
You might have heard that what is the autism rate in America is rising. And it's true! But it's not necessarily because there's more autism now than there used to be.
A big part of it is that we're getting better at identifying it. Diagnostic criteria have evolved, and there's more awareness among parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals. This leads to earlier diagnoses, which means more children are getting the support they need.

What Is ABA Therapy for Autism
ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) therapy is a widely used approach that focuses on teaching new skills and reducing challenging behaviors using principles of learning.
It involves breaking down complex skills into smaller, manageable steps and using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors.
Potential Benefits:
Improved communication skills
Increased social skills
Reduced challenging behaviors
Enhanced adaptive living skills (e.g., self-care, daily routines)
ABA therapy has faced criticism from some members of the autism community, who argue that it can be too focused on "normalizing" autistic individuals and may not always respect their unique needs.
It's important to find qualified and ethical ABA therapists who prioritize the individual's well-being and goals.
The Specificity of Scripting
Scripting refers to the use of pre-planned phrases or sentences in social situations. People with autism may use scripts to navigate social interactions, reduce anxiety, and improve communication.
Why is it Helpful?
Provides a predictable framework for social situations
Reduces the cognitive load of having to come up with responses on the spot
Can help initiate conversations and maintain social interactions





